Special Approaches for Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency:
Polyurethane Rigid Foam-PCM Composite Materials
Studies on renewable energy sources and improved energy efficiency are important for reducing carbon dioxide emissions from petroleum sources. Up to 40% of total energy consumption in the European Union originates from private residences, commercial and public spaces.
Therefore, reducing energy consumption in living spaces without compromising living conditions and indoor thermal comfort limits is important for reducing carbon footprint and developing environmentally friendly green buildings.
The energy need arising from the increasing population and industrialization in our country is rapidly increasing the difference between energy production and consumption. In our country, which is largely foreigndependent in terms of primary energy resources, approximately 74% of the energy is imported from abroad and constitutes the largest current account deficit item.
For this reason, studies on the efficient use and storage of energy make significant contributions to the more efficient use of energy resources in our country. Today, the spread and application of this awareness has gained more importance in all sectors.
When it comes to imbalances in energy consumption, supply and demand, the storage of heat energy gains importance. Today, applications for heating, cooling and the use of waste heat come to the fore, and heat energy storage systems can offer a solution to the imbalance between energy saving and supply and demand.
The most widely used method of storing heat energy is sensible heat storage, which is
observed due to the increase in temperature. The walls and the floor surrounding the room are the volumes where the sensible heat is stored with the increase in temperature in the heating of living environments with hot water circulation radiators or underfloor heating
systems.
However, the phase change of a material and storing heat as latent heat is a much more effective and advantageous method than the sensible heat storage method. While the material changes phase at a constant temperature (or in a narrow temperature range), it absorbs a large amount of heat energy from the environment or gives it to the environment.
Since no perceptible temperature change is observed in the storage of heat energy, it is called latent heat storage. Materials used in latent heat storage are called Phase Change Materials (PCM). The oldest and most common usage examples are applications where ice or snow is used to store cold.
One of the fastest growing groups in the polymer industry in recent years is undoubtedly polyurethanes. Basically, the urethane chain is formed as a result of the reaction of the isocyanate functional group with the hydroxy functional group. It was first synthesized by Otto Bayer and his colleagues in 1937.
While polyester and polyether polyol are commonly used as hydroxy sources in polyurethane commercially, different types of isocyanates are used as aliphatic and aromatic.
Considering the usage areas, it can be seen from aircraft-ship building materials, seat sponges, mattress sponges, packaging foams, fiber, polyurethane rigid foams (insulation materials), toys, wheels, artificial leather, slippers / shoe soles, adhesives, medical applications, etc. has found a wide range of uses.
The biggest reason why polyurethane rigid foams have become popular especially in
the field of insulation in recent years is that they can be used without any joints by using different polyol groups, isocyanate types, glycols and blowing gases. The product can be obtained with the desired heat transmission coefficient, density and hardness values by changing the above-mentioned raw material types, amounts and rates.
Moreover, by using new generation reactive catalysts during the foaming process, catalyst-related emissions are prevented. Rigid polyurethane foams are used extensively in applications such as sandwich panels, refrigerators, cold storage panels, boiler and pipe insulation, tank linings, due to their low thermal conductivity coefficient.

The thermal insulation capabilities of polyurethane rigid foam materials, which have closed cell structures in the foam and low thermal conductivity coefficient values, can be customized by developing PU-PCM composite materials for special applications.
At this point, the aim is to benefit from the energy stored as latent heat by the PCM as it melts by absorbing heat during the increase in ambient temperature for thermal insulation.
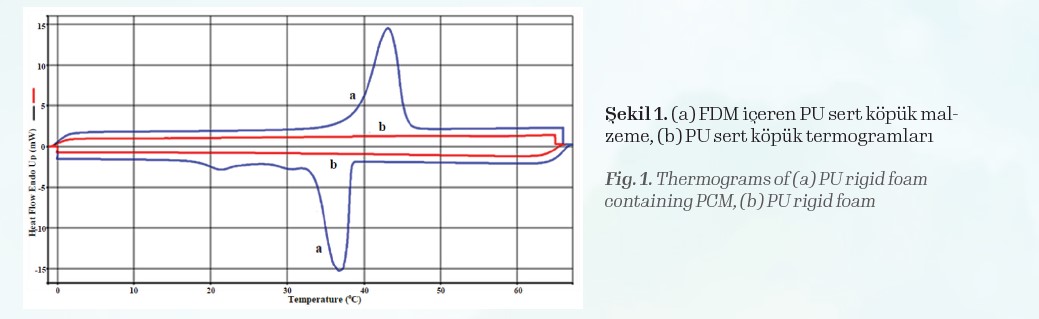
In this way, the PCM in the foam material contributes to the thermal insulation property of the material by accumulating the heat from the ambient temperature increase during melting at a constant temperature (or in a narrow temperature range). This feature that PCM brings to the foam material is clearly seen in the thermogram given in Figure 1.
PCM dispersed homogeneously in the foam structure starts to melt at around 38oC and fulfills the task of storing latent heat in the foam. In the foam sample without PCM, on the other hand, there is no phase transition, but a linear temperature increase occurs.
When the two cases are compared, it has been determined that, depending on the amount of PCM used during the heating of the foam between 5-90oC, it can store 21% to 34% more heat in the form of sensible and latent heat. This shows that PU-PCM foam composite material will buffer more heat for the same thickness in thermal insulation.
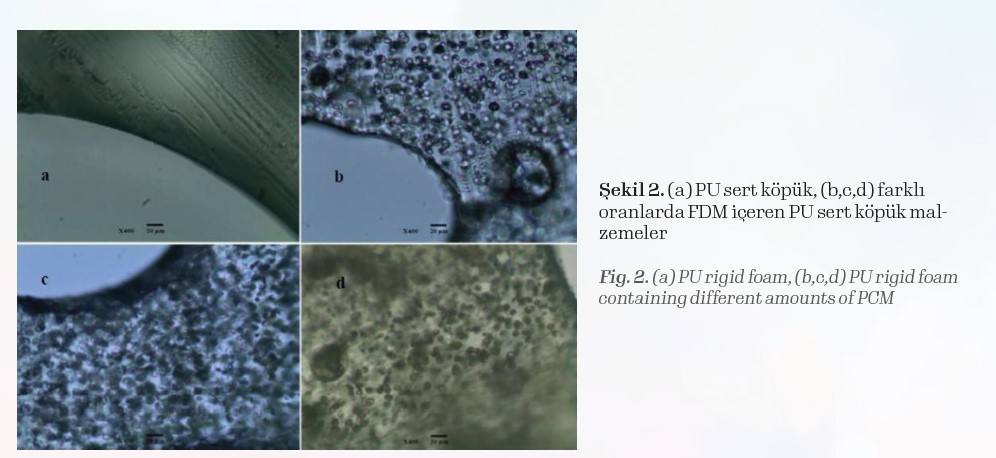
In Figure 2, homogeneously dispersed PCM materials in the foam structure are seen in the x400 magnification microscope images.
The important point here is that the PU-PCM composite formulation is formed in such a way that it affects the closed cell structure of the foam the least. Otherwise, the increase in the thermal conductivity coefficient may cause the desired benefit effect not to be seen.
In such and similar cases, the PCM ratio can be adjusted together with the polyurethane formulation, or different additives can be added to the formulation, which can passively contribute to thermal insulation and reduce the thermal conductivity of the composite
foam material.
As a result, PU-PCM foam composite materials are a current topic open to R&D studies in reducing energy consumption and developing special application materials for energy saving. The content of the subject appeals to a wide range of applications in terms of determining the application areas and the required end product features.
Assoc. Prof. Ahmet Alper Aydın
Lecturer
Chemical Engineering Department
Istanbul Technical University
Dr. Başar Yıldız
General Manager
İdeakim Global Kimya A.Ş.

 The thermal insulation capabilities of polyurethane rigid foam materials, which have closed cell structures in the foam and low thermal conductivity coefficient values, can be customized by developing PU-PCM composite materials for special applications.
At this point, the aim is to benefit from the energy stored as latent heat by the PCM as it melts by absorbing heat during the increase in ambient temperature for thermal insulation.
In this way, the PCM in the foam material contributes to the thermal insulation property of the material by accumulating the heat from the ambient temperature increase during melting at a constant temperature (or in a narrow temperature range). This feature that PCM brings to the foam material is clearly seen in the thermogram given in Figure 1.
PCM dispersed homogeneously in the foam structure starts to melt at around 38oC and fulfills the task of storing latent heat in the foam. In the foam sample without PCM, on the other hand, there is no phase transition, but a linear temperature increase occurs.
When the two cases are compared, it has been determined that, depending on the amount of PCM used during the heating of the foam between 5-90oC, it can store 21% to 34% more heat in the form of sensible and latent heat. This shows that PU-PCM foam composite material will buffer more heat for the same thickness in thermal insulation.
In Figure 2, homogeneously dispersed PCM materials in the foam structure are seen in the x400 magnification microscope images.
The thermal insulation capabilities of polyurethane rigid foam materials, which have closed cell structures in the foam and low thermal conductivity coefficient values, can be customized by developing PU-PCM composite materials for special applications.
At this point, the aim is to benefit from the energy stored as latent heat by the PCM as it melts by absorbing heat during the increase in ambient temperature for thermal insulation.
In this way, the PCM in the foam material contributes to the thermal insulation property of the material by accumulating the heat from the ambient temperature increase during melting at a constant temperature (or in a narrow temperature range). This feature that PCM brings to the foam material is clearly seen in the thermogram given in Figure 1.
PCM dispersed homogeneously in the foam structure starts to melt at around 38oC and fulfills the task of storing latent heat in the foam. In the foam sample without PCM, on the other hand, there is no phase transition, but a linear temperature increase occurs.
When the two cases are compared, it has been determined that, depending on the amount of PCM used during the heating of the foam between 5-90oC, it can store 21% to 34% more heat in the form of sensible and latent heat. This shows that PU-PCM foam composite material will buffer more heat for the same thickness in thermal insulation.
In Figure 2, homogeneously dispersed PCM materials in the foam structure are seen in the x400 magnification microscope images.

 The important point here is that the PU-PCM composite formulation is formed in such a way that it affects the closed cell structure of the foam the least. Otherwise, the increase in the thermal conductivity coefficient may cause the desired benefit effect not to be seen.
In such and similar cases, the PCM ratio can be adjusted together with the polyurethane formulation, or different additives can be added to the formulation, which can passively contribute to thermal insulation and reduce the thermal conductivity of the composite
foam material.
As a result, PU-PCM foam composite materials are a current topic open to R&D studies in reducing energy consumption and developing special application materials for energy saving. The content of the subject appeals to a wide range of applications in terms of determining the application areas and the required end product features.
Assoc. Prof. Ahmet Alper Aydın
Lecturer
Chemical Engineering Department
Istanbul Technical University
Dr. Başar Yıldız
General Manager
İdeakim Global Kimya A.Ş.
The important point here is that the PU-PCM composite formulation is formed in such a way that it affects the closed cell structure of the foam the least. Otherwise, the increase in the thermal conductivity coefficient may cause the desired benefit effect not to be seen.
In such and similar cases, the PCM ratio can be adjusted together with the polyurethane formulation, or different additives can be added to the formulation, which can passively contribute to thermal insulation and reduce the thermal conductivity of the composite
foam material.
As a result, PU-PCM foam composite materials are a current topic open to R&D studies in reducing energy consumption and developing special application materials for energy saving. The content of the subject appeals to a wide range of applications in terms of determining the application areas and the required end product features.
Assoc. Prof. Ahmet Alper Aydın
Lecturer
Chemical Engineering Department
Istanbul Technical University
Dr. Başar Yıldız
General Manager
İdeakim Global Kimya A.Ş.