Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in the form of micronized powders have brought desirable properties for coating and ink applications including excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and low coefficient of friction.
In 2019, the Stockholm Convention began restricting the use of raw materials containing > 25 ppb perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). This global restriction on PFOA and its salts as persistent organic pollutants (POPs) has impacted traditional PTFE. The need for PFOA compliant PTFE or PTFE-free alternatives has been greatly expedited.
In this paper we present new technology that serves as a viable alternative to PTFE. These PTFE-free formulations deliver similar properties to PTFE-containing formulations. These new additives lead to significantly improved mechanical resistance and a significantly low COF and are therefore excellently suited as functional replacements for PTFE-based additives. The advantages of the halogen free additives are characterized by good compatibility in inks and coatings and due to their low density as compared to PTFE, are easier to disperse and process.
1. Introduction
PTFE is a common fluoropolymer used in a wide range of industries and it imparts many desirable properties including exceptional chemical resistance, low coefficient of friction, good resistance to heat and low temperature, and enhanced surface durability. These properties make it especially useful in the coatings industry for applications such as can, coil, and graphic arts. Specifically, the PTFE particles are used create a surface texture that promotes these desired properties which is often termed the “overlay / ball bearing” effect.

Recent regulations on PFOA have impacted the use of PTFE due to common production processes that utilize irradiation to make PTFE. The irradiation process that is used to create the small particle sizes required for the inks industry has also been demonstrated to
create PFOA. Therefore, traditional PTFE will need to be replaced with low-PFOA containing PTFE or PTFEfree alternatives using new low-PFOA PVDF or PVDFfree resins.
Within this new regulatory environment, ink formulators and manufacturers need to be prepared to adapt their inks technologies to be compliant. EU legislation requires that no manufacturer can have a process or put into market any product that has more than 25 parts per billion (ppb) PFOA.
Wax additives (surface modifiers) play an important role in replacing traditional PTFE with low-PFOA containing PTFE or PTFE-free alternatives to meet the technical challenges of reducing or removing PFOA from customer products in multiple ways. PTFE-free surface modifiers have been developed using new and alternative raw materials that are functionally similar to PTFE.
The objective of the present paper is to provide wax additives that can be incorporated into ink formulations as an alternative / substitute for PTFE based waxes currently used in such formulation.
2. Materials and Printing Materials
Leneta 3NT-31 gloss finish coated book printing ink drawdown sheets from Leneta Company (USA) were used as received. Blue pigment concentrates were purchased from Helio Beit GmbH (Germany) and were used as received, without further modification.
Wetting agents, defoamers and surfactants received from Biesterfeld GmbH (Germany). Water-based dispersion of styrene acrylic resin was obtained from Lubrizol (China). The water-based dispersion of styrene acrylic is what is known as the ink “vehicle” and is a
soft, flexible, film forming polymer that upon drying results in the actual ink film. The vehicle serves as a carrier for the pigment and binder to affix the pigment to the printed surface.
Wax Additives and Incorporation
There were 4 different waxes were evaluated. The wax was added to ink formulations via drop-wise addition of the calculated weight of wax, whilst continuously stirring for 10 minutes at room temperature. Wax addition level was 2% based on total formulation weight. Table 1 shows the identity and physical properties of the waxes used. The reference sample contains a PTFE-based wax additive and was used as a benchmark (refence). Sample 1, sample 2 and sample 3 are PTFE-free waxes. The control is an ink formulation without wax.

Printing Preparation
The printed ink films for these studies were made by hand printing inks on Leneta 3NT-31 backside by using a Weller Flexi-Proofer. The Flexi-Proofer consists of a rubber roller that is in contact with an engraved anilox metal roller. Several drops of ink are placed between the two rollers and a simple draw-down consisting of rolling the ink-coated anilox roller on the film was used to print on the paper. Dry film thickness was 5μm. Water-based samples were dried for at least 24 hours at room temperature.
3. Experimental Procedures
To determine the effect of these waxes, rub resistance, gloss and coefficient of friction of the ink with the PTFE-free waxes were analyzed. The testing followed standard test methods used by the industry for evaluating print properties of ink systems. All tests were carried out at room temperature and 50% relative humidity.
Gloss Analysis
Gloss is a function of the substrate, ink formulations and the smoothness of ink film. To test the gloss of the prints, Micro-Tri-Gloss gloss meter (BYK, Germany) was used. Gloss was conducted at 60° & 85° angle of light reflection. The data collection was performed at 3 different positions across the area of the printed ink film and the average values were reported as the final values in terms of gloss units.
The Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction (COF) measurement is a ratio that describes material surface roughness. Param MXD-02 was used to conduct COF. This tester is designed in conformity with the standard ISO 8295-198. All the testing conditions for the measurements followed the ISO standard. As results, the static COF and kinetic COF which are specified in the standard are shown.
Rub Resistance
Sutherland 2000 rub tester with test block weighing 1.82kg was used for determining the rub resistance of printed samples. A printed sample was rubbed back and forth against white unprinted paper at controlled speed for 30 cycles, which corresponds to 60 rubs in total. The white unprinted paper was used to clearly see the ink transference. On the completion, samples were visually inspected to check for ink transfer.
4. Results and Discussion Gloss
Gloss is an important parameter in the printing inks because the gloss affects the print quality providing a better overall better depth of colors. A summary of the results for gloss measured by a gloss meter at 60°and 85° is presented in Figure 1. The results show that the gloss values at 60° for all ink formulation plus waxes are comparable. Ink formulation prepared with wax sample 3 shows slightly higher gloss retention at 60° and 85° compared to the ink formulation without waxes (control formulation) and other samples. This is attributed to surface smoothness of the ink film. These findings also indicate that the PTFE-free wax alternatives are very effective in improving the gloss retention of the printed ink.

The Coefficient of Friction
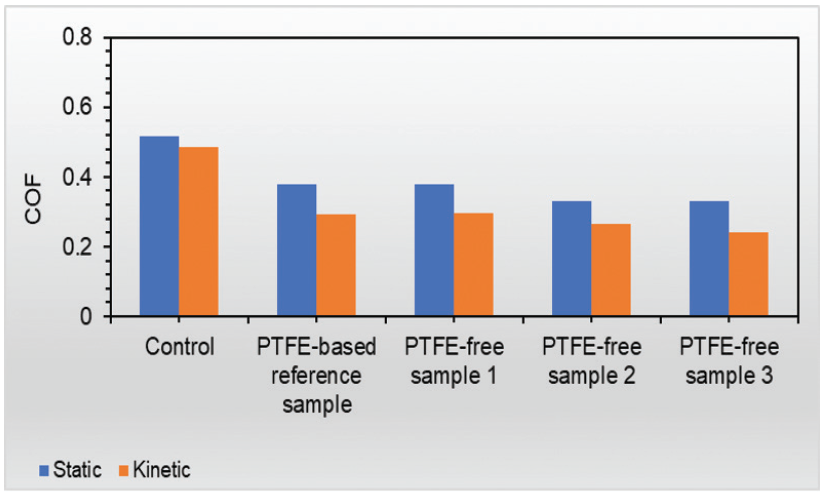
Paper and film packaging COF is an important parameter in the process of printing ink. Controlling COF gives the ability to optimize the performance and avoid problems in forming, transporting and storing packages.
The COF results of ink formulation containing PTFEfree waxes against ink formulation containing PTFEbased wax and control formulation are shown in Figure 2 and the static COF and kinetic COF were compared. The data clearly shows the reduction in both static and kinetic COF for the formulation containing waxes, indicating good film slip. Additionally, formulation containing PTFE-free waxes showed comparable results to formulation with wax PTFE.
Rub Resistance Measurements
After series of rub tests, samples of white papers were then visually evaluated with respect to transferred ink amount on the white unprinted paper. The visual rating scale is 1 to 10, with 1 being a high degree of ink transfer (1=very poor) and 10 being no ink transfer (10=excellent).
The results determined from the visual inspection of the rubs shown in Figure 3 indicate that the formulation containing waxes demonstrated improved rub resistance compared to the control formulation containing no wax.

Figure 4 shows images of rub off test results. From the images we can see that ink transfer onto the white uncoated paper was only extremely strong with ink formulation without waxes indicating insufficient ink resistance to the rub off process. Ink formulations that included waxes showed slight ink transfer indicating high rub resistance. The increased rub resistance with the new wax additives without PTFE is presumably an effect of the improved mechanical properties.
Moreover, it can be seen from Figure 3 and Figure 4 that PTFE- free additives improved the rub resistance of the ink formulations as effectively as commercially available waxes containing PTFE.

Conclusion
The PTFE-free waxes offer a number of benefits when used as a replacement for waxes containing PTFE. When these waxes are incorporated into an ink formulation it not only improves the gloss retention, but also reduces the coefficient of friction and the rub resistance. The results demonstrated that these PTFE-free additives have the potential to be used as alternatives to PTFE-based products.




